Last Updated on September 16, 2025 by andrewshih
PMP Formulas Cheat Sheet
The PMP cheat sheet is aligned with the PMP PMBOK 7 and includes the PMP exam formulas that you will need to know to pass the PMP exam.
Cost Management Formulas
| PV | Planned Value |
| EV | Earned Value |
| AC | Actual Cost |
| BAC | Budget at Completion |
| EAC | Estimate at Completion |
Use the chart to help you understand the cost management formulas.
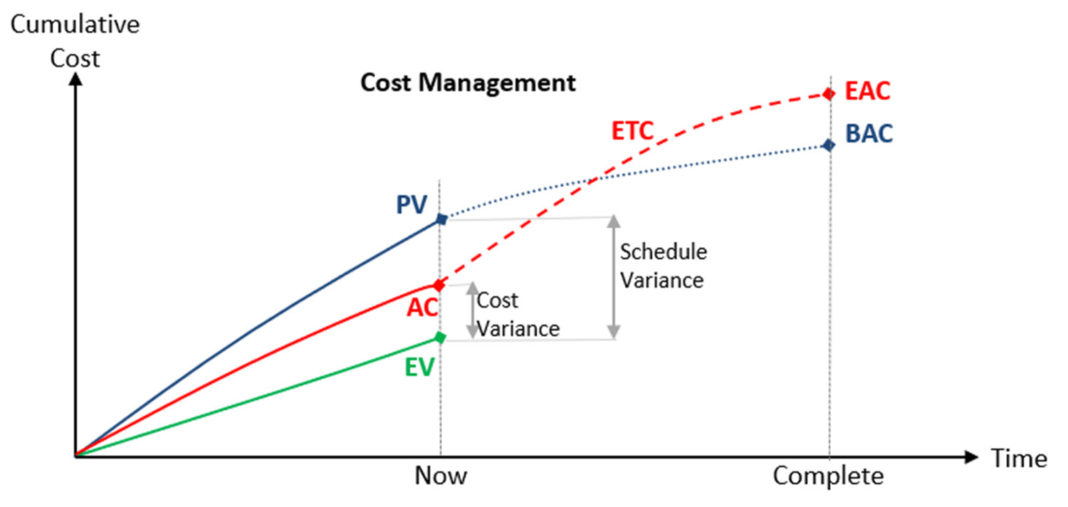
| Cost Variance: CV = EV – AC | |
| The amount of budget deficit or surplus | + = Under planned cost 0 = On planned cost – = Over plan cost |
| Schedule Variance: SV = EV – PV | |
| The amount by which the project is ahead or behind the planned delivery date. | + = Ahead of Schedule 0 = On Schedule – = Behind Schedule |
| Variance at Completion: VAC = BAC – EAC | |
| A projection of the amount of budget deficit or surplus. | + = Under Planned Cost 0 = On Planned Cost – = Over Planned Cost |
| Cost Performance Index: CPI = EV / AC | |
| Shows the percentage of how much costs are over or under the amount of work accomplished. | Greater than 1.0 = Under planned cost 1.0 = On planned cost Less than 1.0 = Over planned cost |
| Schedule Performance Index: SPI = EV / PV | |
| A measure of schedule efficiency. | Greater than 1.0 = Ahead of Schedule 1.0 = On Schedule Less than 1.0 = Behind Schedule |
| Estimate at Completion: The expected total cost of completing all work expressed as the sum of the actual cost to date and estimate to complete. | |
| EAC = AC + ETC | If the initial plan is no longer valid. Use new estimate. |
| EAC = AC+BAC-EV | If the future work will be accomplished at the planned rate, use the remaining budget. |
| EAC = BAC/CPI | If CPI is expected to be the same for the remainder of the project. |
| EAC = AC+(BAC-EV)/(CPI*SPI) | If both CPI and SPI influence the remaining work. |
| Estimate to Complete: The expected cost to finish all remaining project work. | |
| ETC = EAC – AC | Assuming the work is proceeding on plan |
| To Complete Performance Index: A measure of the cost performance that must be achieved with the remaining resource in order to meet a specific management goal. | |
| TCPI = remaining work/budget available | Greater than 1.0 = Harder to complete 1.0 = Same to complete Less than 1.0 = Easier to complete |
| TCPI = (BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) | The efficiency that must be maintained in order to complete on plan |
| TCPI = (BAC-EV)/(EAC-AC) | The efficiency that must be maintained in order to complete the current EAC. |
Schedule Management Formulas
| PERT Weighted Average = (O+4M+P)/6 |
| PERT Standard Deviation = (P-O)/6 |
| Project Evaluation & Review Technique for estimating activity duration. O=optimistic, M=Most likely, P=Pessimistic |
| Float (or slack) = LS – ES Float (or slack) = LF – EF | LS = Late Start ES = Early Start LF = Late Finish EF = Early Finish |
Communication Management Formulas
| Communication Channels = N(N-1)/2 |
Need more than just a PMP formulas cheat sheet?
If you are looking for a more comprehensive preparation of all the formula questions that may appear on the PMP exam, PM-Prepcast formula package will be your best bet.
PM-Prepcast Formula Package $29.00
Build your ability to interpret results instead of memorizing complex calculations.
Highlights:
- A clear, step-by-step guide to understanding formulas and interpreting outcomes
- Includes 160 practice questions, with 70 focused on interpretation
- Aligned with the latest PMP exam format and formula question types
Benefits:
- Gain confidence in solving interpretive questions, a key part of the PMP exam
- Learn the formulas, understand the math, and sharpen your analytical skills
- Be fully prepared for any formula-related question you might face on exam day
Additional PM Exam Resource
In addition to this PMP Formulas Cheat Sheet, you may want to check out the resource page for recommended resources and links to a collection of free exam questions. If you are looking for a study guide, check out the PMP Study Guide with Pros/Cons of most popular PMP books, including Rita Mulcahy, Andy Crowe, and Head First PMP.