Last Updated on June 9, 2024 by andrewshih
Understanding and effectively managing resources is critical in project management. One essential tool for this is the Resource Breakdown Structure. RBS provides a detailed hierarchical representation of resources required for a project.
This guide will help you grasp the concept, and help you create an effective RBS with examples, templates, and a case study.
- What is Resource Breakdown Structure?
- How does RBS work?
- Benefits of Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- Weaknesses of Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- Key Components of RBS
- Steps to Create an RBS with Examples
- Resource Breakdown Examples
- Resource Breakdown Structure Templates
- Tips for Creating an Effective Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- Mistakes to Avoid When Creating an RBS
- Working with RBS and WBS
- Case Study for Using Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- Next Step
- FAQs for Resource Breakdown Structure
What is Resource Breakdown Structure?
The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a visual tool that categorizes and details all the resources needed for a project. It includes human resources, equipment, materials, and financial resources. An RBS helps in resource planning and ensures that all necessary resources are accounted for.
How does RBS work?
An RBS works by breaking down the project into manageable components and detailing the resources needed for each. This hierarchical structure facilitates better coordination and communication among project stakeholders.
Benefits of Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
By utilizing an RBS, project managers can ensure that all resources are accounted for, managed efficiently, and utilized effectively to support the successful completion of the project.
-
Enhanced Project Visibility: Provides a clear overview of all resource requirements, making it easier to plan and manage the project effectively.
-
Improved Resource Allocation: Ensures that resources are allocated appropriately, avoiding overuse or underuse of any resource.
-
Facilitate Risk Management: Identifies potential resource shortages or surpluses early in the project, allowing for proactive risk management and mitigation.
-
Efficient Resource Utilization: Helps in optimizing the use of resources, reducing waste, and ensuring that the project stays within budget.
-
Better Communication: Facilitates clear communication among project stakeholders by providing a detailed breakdown of resource needs.
-
Streamlined Project Planning: Aids in developing a comprehensive project plan by detailing all necessary resources and their interrelationships.
-
Support for Decision Making: Provides valuable data for making informed decisions about resource allocation, budgeting, and project scheduling.
Weaknesses of Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
While there are many benefits of using RBS, the document has limitations as well.
-
Time-Consuming to Create: Developing a comprehensive RBS can be labor-intensive, especially for large or complex projects.
-
Requires Regular Updates: As projects evolve, the RBS must be frequently updated to reflect changes, which can be cumbersome.
-
Potential for Over-Detailing: There’s a risk of becoming too detailed, which can make the RBS difficult to manage and use effectively.
-
Dependence on Accurate Data: The effectiveness of an RBS relies heavily on the accuracy of the initial data. Inaccurate resource identification can lead to poor planning.
-
Complexity in Large Projects: For very large projects, managing an extensive RBS can become overly complex and unwieldy.
Key Components of RBS
An effective RBS typically includes the following components:
Human Resources: This includes all the personnel involved in the project, such as project managers, team members, contractors, and consultants.
Equipment: All the tools, machinery, and equipment necessary for completing project tasks are listed here.
Materials: This category covers all raw materials and supplies needed for the project.
Financial Resources: Budgetary allocations and financial resources required to support the project activities are detailed in this component.
Other Resources: This includes additional assets such as time, technology, and any other necessary resources specific to the project.
Steps to Create an RBS with Examples
Step 1: Planning Stage
Define the project scope and objectives to understand the overall resource needs.
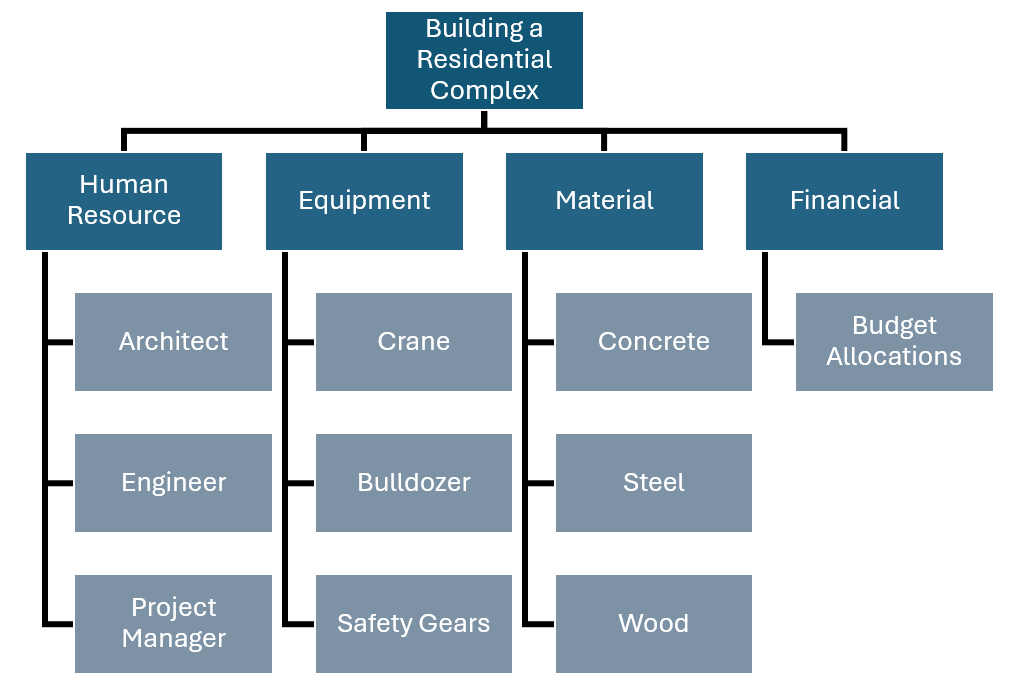
Example: For a construction project, the scope might include building a residential complex, requiring a clear understanding of all phases involved.
Step 2: Resource Identification
List all necessary resources required for the project.
Example: Identify resources such as architects, engineers, construction workers, concrete, steel, cranes, and financial allocations.
Step 3: Resource Categorization
Group resources into categories.
Example: Categorize resources into Human Resources (architects, engineers), Equipment (cranes, bulldozers), Materials (concrete, steel), and Financial Resources (budget allocations).
Step 4: Creating the RBS Structure
Develop a visual representation or template to organize resources hierarchically.
Example: Create a tree diagram with the top-level categories branching out into specific resources, such as human resources branching into architects and engineers.
Step 5: Review and Validation
Verify the accuracy and completeness of the RBS.
Example: Engage project stakeholders to review the RBS and ensure all resources are captured, making adjustments based on feedback.
Resource Breakdown Examples
Construction Industry RBS Example
In construction projects, an RBS helps in meticulously planning and managing resources such as labor, materials, and equipment. This ensures that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
To illustrate, let’s consider a construction project:
- Human Resources: Engineers, laborers, project managers.
- Equipment: Cranes, bulldozers, safety gear.
- Materials: Concrete, steel, wood.
- Financial Resources: Budget allocations for different phases.
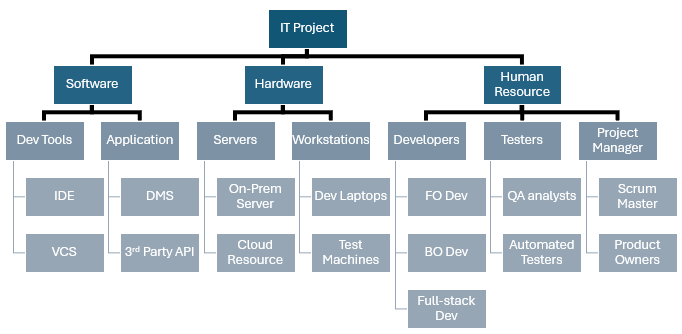
IT Projects RBS Example
In IT projects, an RBS can help manage the various technical and human resources required to develop, test, and deploy software applications.
- Software:
- Development Tools: IDEs (Integrated Development Environments), version control systems.
- Applications: Database management systems, third-party APIs.
- Hardware:
- Servers: On-premises servers, cloud computing resources.
- Workstations: Developer laptops, testing machines.
- Human Expertise:
- Developers: Front-end developers, back-end developers, full-stack developers.
- Testers: QA analysts, automated testers.
- Project Managers: Scrum masters, product owners.
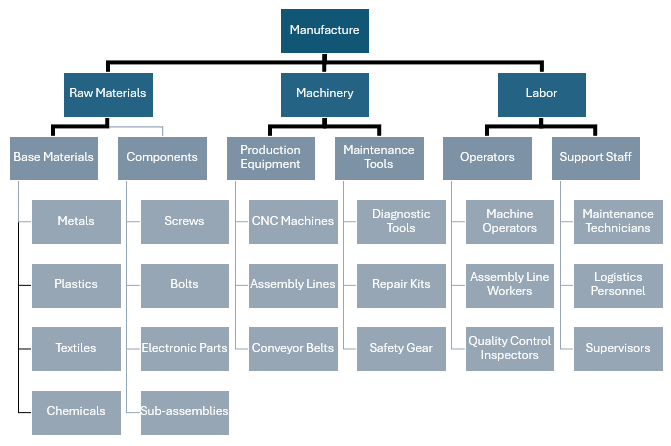
Manufacturing Industry RBS Example
In manufacturing, an RBS helps in organizing and managing the various materials, machinery, and labor needed to produce goods.
- Raw Materials:
- Base Materials: Metals, plastics, textiles, chemicals.
- Components: Screws, bolts, electronic parts, sub-assemblies.
- Machinery:
- Production Equipment: CNC machines, assembly lines, conveyor belts.
- Maintenance Tools: Diagnostic tools, repair kits, safety gear.
- Labor:
- Operators: Machine operators, assembly line workers, quality control inspectors.
- Support Staff: Maintenance technicians, logistics personnel, supervisors.
Resource Breakdown Structure Templates
Resource Breakdown Structure PowerPoint Template
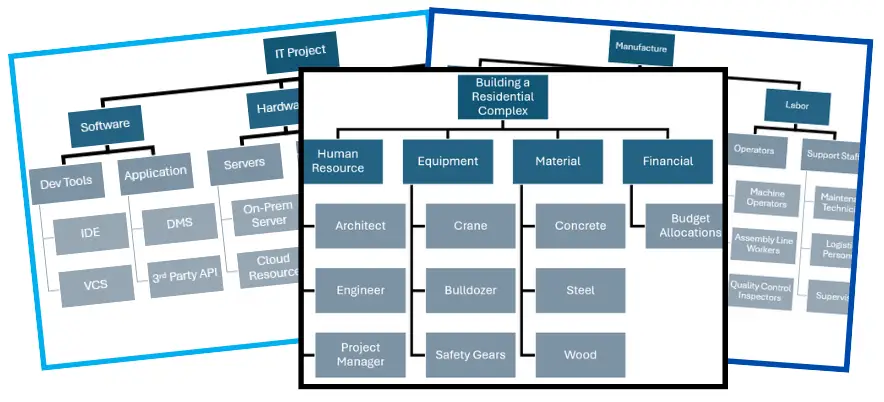
You can download the Resource Breakdown Structure examples above for Construction, IT Project, and Manufacture templates in Powerpoint format.
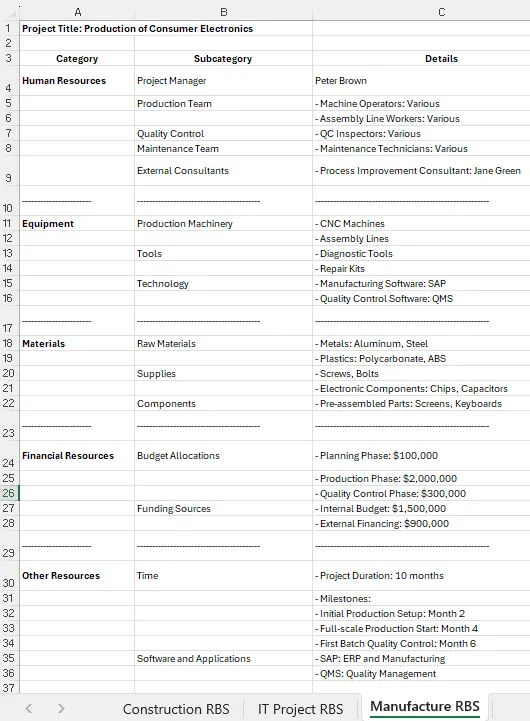
Resource Breakdown Structure Excel Template
The Construction, IT Project, and Manufacture Resource Breakdown Structure templates are also available in Excel format. This format is available with sample data as illustration.
Tips for Creating an Effective Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
-
Start with Clear Project Objectives: Ensure that the project’s goals and deliverables are well-defined before breaking down resources.
-
Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage team members and stakeholders in the process to gain insights and ensure that all necessary resources are identified.
-
Use a Hierarchical Structure: Organize resources in a hierarchical manner, categorizing them into broader categories and then into more specific subcategories.
-
Maintain Flexibility: Design the RBS to be adaptable to changes in project scope or resource availability.
-
Regularly Update the RBS: Review and revise the RBS periodically to reflect any changes in the project plan or resource needs.
-
Leverage Tools and Templates: Use project management software and templates to streamline the creation and management of the RBS.
-
Ensure Clear Labeling: Clearly label each resource and subcategory to avoid confusion and ensure easy reference.
-
Align with Project Schedule: Integrate the RBS with the project schedule to ensure that resource allocation aligns with project timelines.
-
Document Assumptions and Constraints: Clearly document any assumptions or constraints related to resource availability or usage.
Mistakes to Avoid When Creating an RBS
-
Over-Detailing: Avoid making the RBS too detailed, as it can become unmanageable and difficult to use.
-
Ignoring Stakeholder Input: Failing to involve key stakeholders can result in missing critical resources or misaligned expectations.
-
Inconsistent Categorization: Ensure that resources are categorized consistently to avoid confusion and mismanagement.
-
Static RBS: Do not treat the RBS as a static document; it should be regularly updated to reflect project changes.
-
Omitting Resource Types: Ensure that all resource types are included; omitting any type can lead to incomplete planning.
-
Lack of Documentation: Failing to document the rationale behind resource allocations and categories can lead to misunderstandings later.
-
Poor Integration with Other Plans: Ensure the RBS is integrated with other project management plans, such as the work breakdown structure (WBS) and project schedule.
-
Ignoring Resource Risks: Failing to identify and plan for potential resource risks can result in project delays and cost overruns.
-
Neglecting Resource Availability: Ensure that the availability of resources is considered and documented to avoid conflicts and shortages.
-
Underestimating Resource Needs: Be realistic about the quantity and type of resources required to prevent resource shortages during project execution.
Working with RBS and WBS
Here is a good short video that explains how the Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) works together with Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to create the Resource Assignment Matrix (aka RACI chart).
Case Study for Using Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
Project: Building a Residential Complex
Overview: A construction company undertook a project to build a residential complex. The project included various phases such as foundation work, framing, electrical installation, and plumbing.
RBS Implementation:
- Human Resources: Project managers, engineers, designers, construction workers
- Equipment: Cranes, bulldozers, power tools
- Materials: Concrete, steel, wiring
- Financial Resources: Budget allocations for each phase
Outcome: Using RBS improved resource allocation, prevented overallocation, and optimized resource utilization. The project was completed on time and within budget, demonstrating the efficiency of RBS in resource management (Source: PMI UK).
Next Step
A Resource Breakdown Structure is an indispensable tool in project management, offering clarity, improving efficiency, and aiding in risk management.
By understanding and implementing an RBS, project managers can ensure that all resources are effectively planned and utilized, leading to the successful completion of projects. This structured approach not only enhances project visibility but also ensures that resources are managed in the most efficient manner possible.
To complement RBS, check out Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and RACI Chart next.
FAQs for Resource Breakdown Structure
What is the difference between RBS and WBS?
The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) focuses on categorizing and detailing all resources needed for a project, such as human resources, equipment, materials, and finances.
In contrast, the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) breaks down the project into smaller tasks and deliverables, providing a detailed roadmap of what needs to be done. Together, they provide an important framework for planning and executing a project.
Who is responsible for creating the Resource Breakdown Structure?
The project manager is primarily responsible for creating the RBS, but it is a collaborative effort involving the project team and key stakeholders. The project manager coordinates with team members to identify and categorize resources, ensuring the RBS is comprehensive and accurate.
How often should the RBS be updated?
The RBS should be updated regularly to reflect changes in project scope, resource availability, and any adjustments needed for effective resource management. Regular reviews, such as at the end of each project phase or during periodic project reviews, help maintain its accuracy and relevance throughout the project lifecycle.